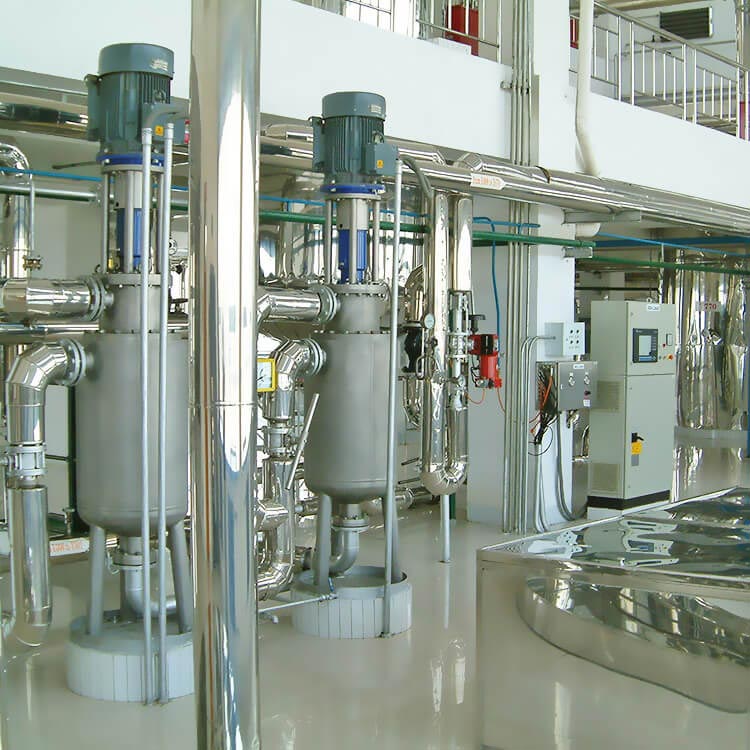
Overview
The purpose of oil bleaching is not to theoretically remove all pigments but to improve the color of the oil and provide qualified materials for oil deodorization. What's more, the decolorization section can avoid oil color reversion and improve the oil product's shelf life.
Features
The main composition of the edible oil is triglycerides. Pure triglyceride liquid is colorless and they become white when in solid form. But the common oil has different colors due to different amounts and varieties of pigments in oil, the pigments can be divided into three categories: Organic pigments such as chlorophyll, carotenoids, and gossypol; Organic degradants such as proteins, carbohydrates, and phospholipids; Some chromogens. Not all the pigments are bad, but the harmful pigments would damage oil quality and threaten human health, which should be removed.

In industrial cooking oil production plants, there are many methods for oil decolorization: adsorption decolorization, heating decolorization, oxidation decolorization, chemical reagent decolorization, and so on. Among them, adsorption decolorization is the mostly method in oil refining processes
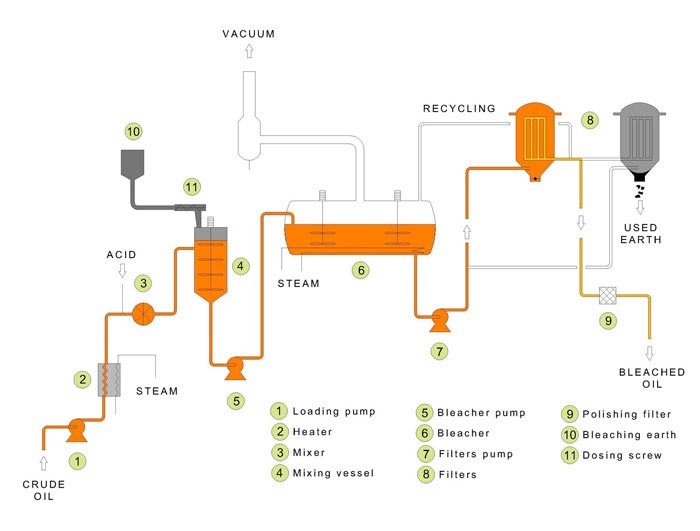
Oil adsorption decolorization is making use of some substances that have a strong adsorption effect on pigments(such as bleaching earth, activated clay, and activated carbon)to adsorb pigments and other impurities in oil under certain conditions. Adsorption decolorization can not only achieve the purposes of improving oil color and removing gum but also effectively remove trace metal ions in oil and some substances that cause the poisoning of hydrogenated catalysts,so as to provide a good condition for further oil refining (hydrogenation, deodorization).
Thermal decolorization is a decolorizing method that uses the thermal denaturation of certain heat-sensitive pigments to achieve decolorization by heating. However, high temperature inevitably leads to thermal oxidation of the oil. Therefore, this method is limited to the auxiliary decoloration of some low-value oil containing heat-sensitive dyes (palm oil, coconut oil), and is not used as a normal process for oil refining.
Air decolorization makes use of chromophores'instability on oxygen to decolorize the oil by air-oxidizing pigments. For example, the carotenoids and chlorophyll in the oil are very unstable because of their structure, which is easily discolored under the action of oxygen. However, air decolorization leads to thermal oxidation of the oil, too. Thus, this method is generally limited to the auxiliary decolorization of high-carotene oil (such as palm oil).
Reagent decolorization is a bleaching method that uses chemical reagents for oxidation and decolorization of the chromophores. The commonly used oxidants are sodium dichromate, hydrogen peroxide, and ozone. But reagent decolorization method has a residual problem with chemical reagents, therefore, the bleaching process and washing separation conditions should be strictly controlled during operation, so that the residual amount of reagent can be controlled within the allowable range.
| Continuous type | ||||
| Category of comparison | Intermittent type | Tube type | Mechanical mixing | Steam stirring |
| Clay consumption (%) | 3-5 | 1-3 | 3-5 | 1-3 |
| Decolorization temperature (℃) | 90-110 | 100-110 | 90-110 | 105-120 |
| Decolorization time (min) | 30-50 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 20-30 |
| Decolorizing vacuum degree (MPa) | -0.095 | -0.095 | -0.095 | -0.095 |
| Bleaching oil color (Lovibond color) | Y35R6 | Y35R4 | Y35R6 | Y35R4 |
| Equipment cost | High | Low | High | Low |
| Equipment maintenance cost | High | Low | High | Low |
| Steam consumption (%) | 5 | 2-3 | 3 | 2-4 |
| Power consumption | High | None | High | None |
Copyright @ Henan Huatai Cereals And Oils Machinery Co.,Ltd.
